Johannes Kepler Space Astronomy Physics
Planetary Motion
- Path of an object through space is called an orbit
- Ptolemy's geocentric model was accepted until Copernicus' heliocentric model finally got adopted
- Johannes Kepler's laws and moving to ellipses helped adoption
Johannes Kepler's Three Laws of Orbits
- Each planet orbits the Sun in an ellipse
- Straight line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas in space and equal areas in time
- Eg. in 60 days a planet will move the same amount of area, no matter how close it is to the body it orbits
- The Law of Equal Areas
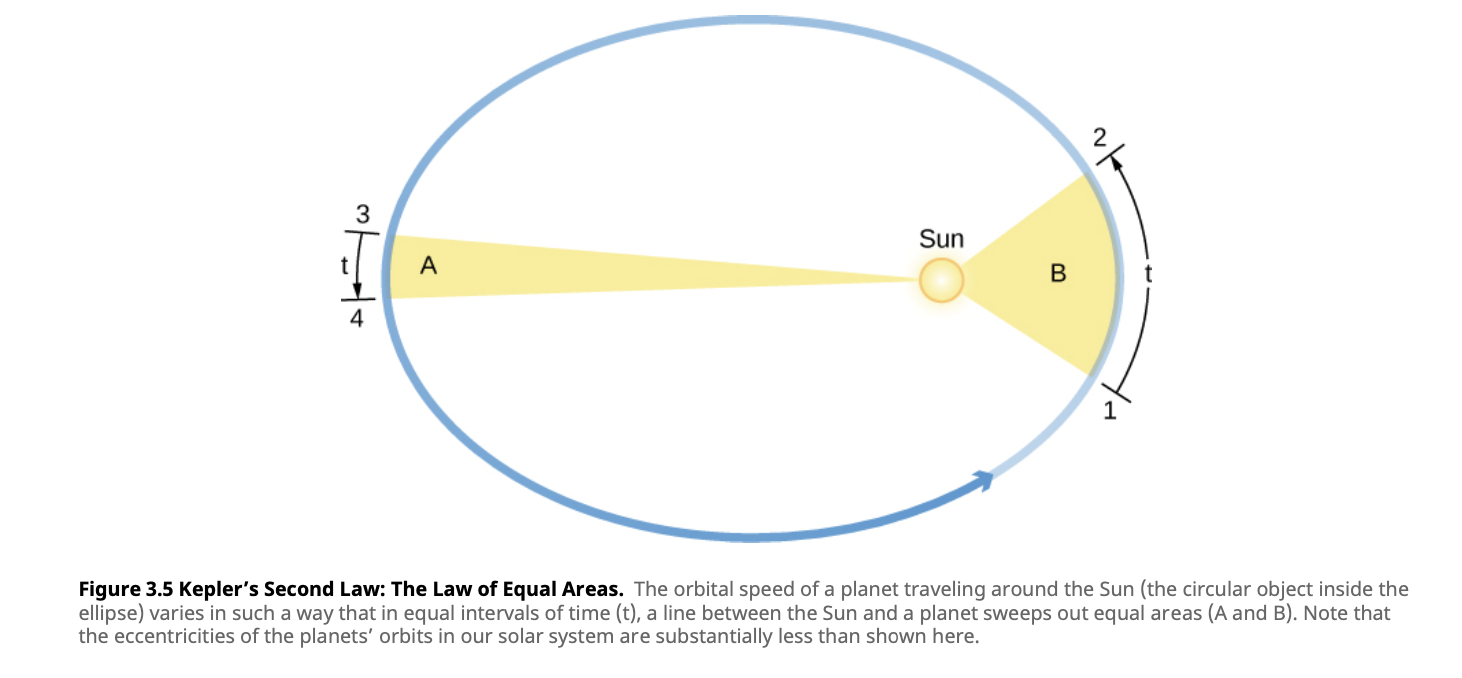
- Discovered by observing orbits speeding up as a planet gets closer to the Sun
- Consequence of the conservation of angular momentum
- Figure skater law
- A planet's orbital period ($P$) squared is proportional to the semi-major axis ($a$) of its orbit cubed
- $P^2 \propto a^3$
- When $P$ is measured in years and $a$ is measured in astronomical units, the two sides are equal
- Applies to all objects orbiting the Sun
- Provides means for calculating objects relative distances from the Sun
- Law of harmonies