Circuit
- A bunch of logic gates combined
- Output of one gate --> input of another
- Flow of electricity is controlled by the interacting gates
- Equivalent when they produce the same output for identical input
Combinational Circuits
- Circuit whose output is solely determined by its input values
Sequential Circuits
- Circuit whose output is a function of its input values and the current state of the circuit
Adders
- Performs addition operation on binary values
Half Adder
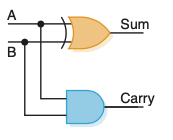
- Computes the sum of two bits and produces the appropriate carry bit
- An
XOR and an AND gate
- Doesn't allow a possible carry coming in the calculation
Full Adder
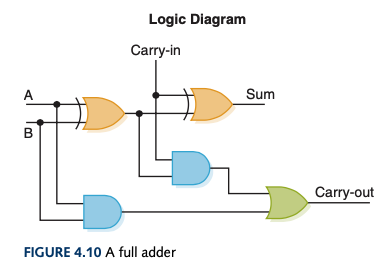
- Computes the sum of two bits, taking an input carry bit into account
Multiplexers
- Input control signals determine which input is routed to its output
- Often called a mux
- Values on $n$ input control lines determine which of $2^n$ other data lines are selected for output
- Demultiplexer (demux) is the opposite of a mux
- Single input --> one of $2^n$ outputs depending on values of $n$ control lines
Circuits as Memory
- Can store information
- Sequential circuit
- Output serves as input
- Existing state of circuit is used to determine next state
S-R Latch

- Stores single bit
- Guarantees two outputs ($X$ and $Y$) are always complements of each other
Integrated Circuits
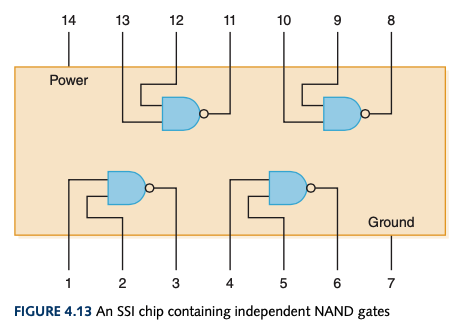
| Abbreviation | Name | Number of Gates |
|---|
| SSI | Small-scale integration | 1 to 10 |
| MSI | Medium-scale integration | 10 to 100 |
| LSI | Large-scale integration | 100 to 100,000 |
| VLSI | Very-large-scale integration | >100,000 |
Electricity Computer Science



