Computing Systems
- Dynamic entity used to solve problems
- Composed of hardware, software, and data
- Hardware: physical elements of computing system
- Software: Programs providing instructions for system to execute
Layers
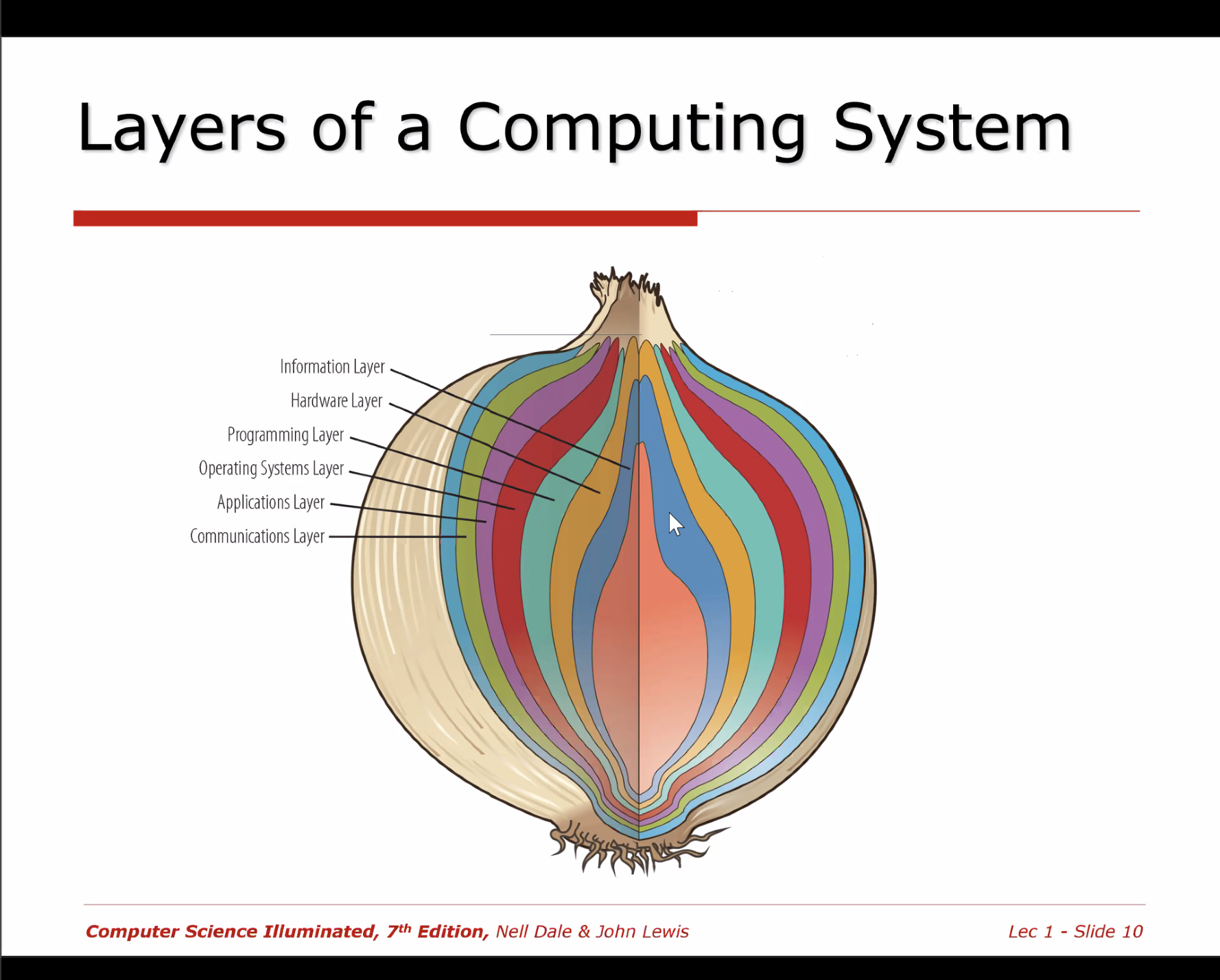
- Information Layer
- The way we represent information
- Mostly conceptual
- Hardware Layer
- Programming Layer
- Operating Systems Layer
- Help us interact with the computer system
- Manage the way hardware, programs, and data interact
- Applications Layer
- Using the computer to solve real world problems
- Communications Layer
Prefixes
| Power of 10 | Power of 2 | Value of Power of 2 | Prefix | Abbreviation | Derivation |
|---|
| $10^{-12}$ | | | pico- | p | Italian for little |
| $10^{-9}$ | | | nano- | n | Greek for dwarf |
| $10^{-6}$ | | | micro- | μ | Greek for small |
| $10^{-3}$ | | | milli- | m | Latin for thousandth |
| $10^{3}$ | 2^{10} | 1024 | kilo- | K | Greek for thousand |
| $10^{6}$ | 2^{20} | 1,048,576 | mega- | M | Greek for large |
| $10^{9}$ | 2^{30} | 1,073,741,824 | giga- | G | Greek for giant |
| $10^{12}$ | 2^{40} | not enough room | tera- | T | Greek for monster |
| $10^{15}$ | 2^{50} | not enough room | peta- | P | Greek for five |
Computer Science
