- Abacus
- Important people
- Harvard Mark I, ENIAC, UNIVAC I
- Early computers
- Launched new era of maths, physics, engineering, and economics
Hardware
First Generation Hardware (1951-1959)
- Vacuum tubes
- Large
- Not reliable
- Lots of heat
- Magnetic drum
- Memory device that rotated under read/write head
- When memory cell was under head, data could be read/written
- Very manual
- Card readers --> magnetic tape drives
- Card readers that read holes punched in a card
- Sequential auxiliary storage devices
- Audio cassettes
Second Generation Hardware (1959-1965)
- Transistor
- Replaced vacuum tube
- Fast, small, durable, cheap
- Nobel prize was rewarded for invention
- Magnetic cores
- Replaced magnetic drums
- Information is available instantly
- CPU no longer has to wait for drum to get to proper place to read/write
- Magnetic disks
- Replaced magnetic tape
- Data accessed directly
- Faster because you can refer to location of data
Third Generation Hardware (1965-1971)
- Integrated circuits
- Replaced circuit boards
- Smaller, cheaper, faster, more reliable
- Solid silicon containing transistors and other components
- Boards were printed
- Transistors
- Now used for memory construction
- One transistor = one bit of information
- Terminal
- Input/output device with keyboard and screen
- Direct access to computer + immediate response
Fourth Generation Hardware (1971-Present)
- Large-scale integration (LSI)
- Great advances in chip tech
- PCs, commercial market, workstations
- Computers become affordable
- Huge companies like Apple, Sun, Dell, etc.
- Laptops, tablets, and smart phones
- Parallel computing
- Networking
- Ethernet used to connect computers
- Resources can be shared over the network
- Cloud computing
Software
First Generation Software (1951-1959)
- Machine language
- Assembly languages and translators
- Programs written using mnemonics
- Mnemonics get translated to machine code
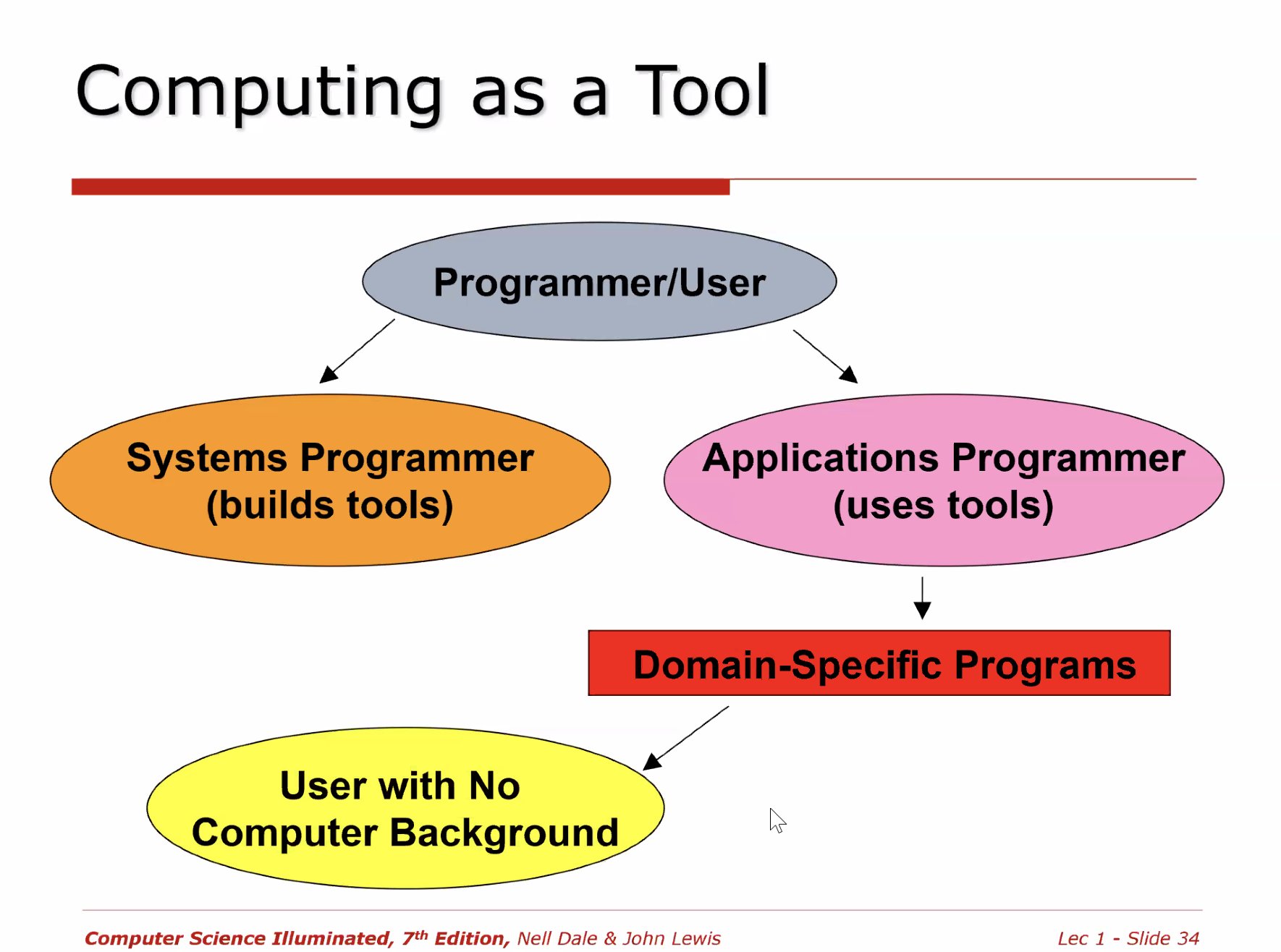
- Programmers split into two groups
- Application programmers
- Systems programmers
Second Generation Software (1959-1956)
Third Generation Software (1965-1971)
- Systems software
- Separation between users and hardware
- Software is being written for general public
Fourth Generation Software (1971–1989)
- Structured programming
- New application software for users
- Spreadsheets
- Word processors
- DBMS
Fifth Generation Software (1990-Present)
Computing as a Discipline
- What can be efficiently automated?
- Four necessary skills:
- Algorithmic thinking
- Express problems in terms of step-by-step procedures
- Representation
- Store data in a way it can be process efficiently
- Programming
- Algorithmic thinking + Representation --> computer software
- Design
- Software that serves a purpose
Computer Science History
