TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
- Allows ordered, reliable data delivery between computers over the a network
- Creates a connection (see below)
- Built on top of IP
- Operates in the transport layer
- Connection-oriented
- Ensures a connection or session is established by using a three-step process (three-way handshake)
- Helps resolve the issues with IP's connectionless problems
- Sequencing and checksums
- Sends a character string called a checksum that is checked by destination host alone with sequence number for each segment
- Flow control
- Gauges rate of transmission based on how quickly recipient can accept data
- After three initial messages, payload/data is sent
- Sequence numbers will be increased by number of bits included in each received segment
- Confirms correct length of message was received
Three-way handshake
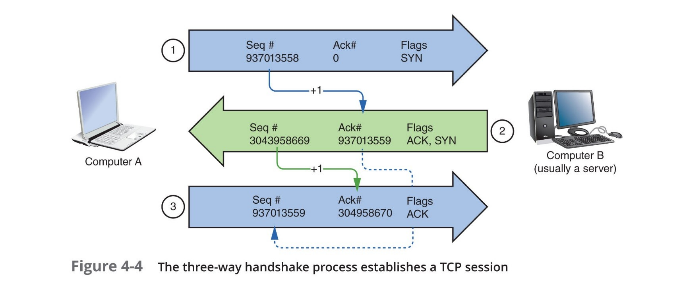
- Request for a connection (SYN)
- Response to request (SYN/ACK)
- Connection established (ACK)
Networking Computer Science TCP-IP
