IP (Internet Protocol)
- Operates at the network layer
- Specifies where data should be delivered
- Identifies the data's source and destination IP addresses
- Enables TCP/IP to internetwork to traverse:
- More than one LAN segment
- More than one type of network through router
- Unreliable, connectionless
- Does not guarantee delivery of data
- No session established before data is transmitted
- Depends on TCP:
- To ensure messages are put back together in proper order
- To ensure each message reaches the correct application on receiving host
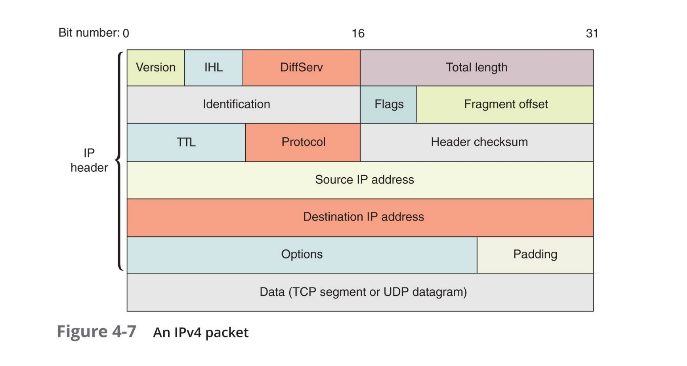
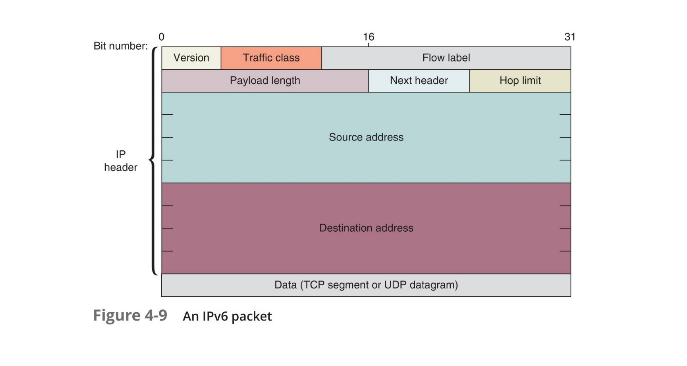
IP Packet
- The smallest unit used to describe data being sent over IP (aside from bytes)
- $2^{16}$ bytes
- Consists of:
IPv4 Packet
IPv6 Packet
Networking Computer Science TCP-IP

