Wireless Networking
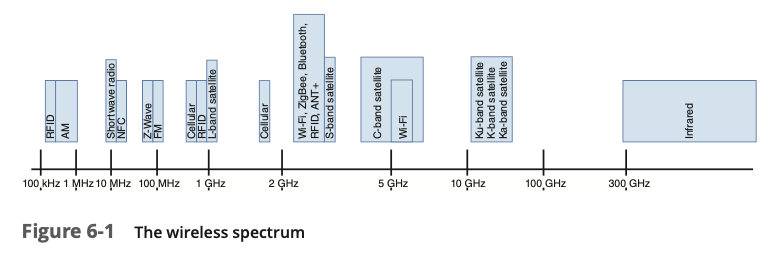
- Most wireless devices implement one of two technologies:
- FHSS (frequency hopping spread spectrum)
- Frequency hopping
- Short bursts of data are transmitted on particular frequency within the band
- Next burst goes to next frequency in a sequence
- Cheaper to implement than DSSS
- More effective than DSSS in crowded/indoor environments
- DSSS (direct sequence spread spectrum)
- Data streams divided and encoded into small chunks (chips)
- Chips are spread over all available frequencies within one of three channels all at the same time
- Wireless standards in various bands
- Wi-Fi --> DSSS
- Bluetooth --> FHSS
- ZigBee --> DSSS
- ANT+ uses fixed frequency (neither DSSS or FHSS)
Antennas
- Used to provide a path for signals to travel
- Air doesn't provide a path like cables would
- Signals originate from electrical current traveling along a conductor
- Travels from transmitter to antenna
- Antenna emits signal as a series of electromagnetic waves
- Signal moves through air to destination
- At destination, another antenna accepts the signal and a receiver converts it to current
- Two antennas must be tuned to the same frequency to communicate
- Each type of wireless service requires an antenna specifically designed for that service
Radiation Pattern
- Relative strength over 3D area of all electromagnetic energy that antenna sends/receives
- Unidirectional
- Directional
- Issues wireless signals along single direction
- Omnidirectional
- Sends/receives wireless signals with equal strength/clarity in all directions
Signal Propagation
- Way in which wave travels from one point to another
- LOS (line of site)
- Ideal signal path
- Signal travels in straight line directly from transmitter to receiver
- Maximizes distance for amount of energy used
- Results in clearest possible signal
- When obstacles are in the way, signal may:
- Pass through obstacle
- Be absorbed
- Fading
- Energy fades as it runs into obstacles
- Excessive fading can cause dropped connections or slow transmission
- Attenuation
- Signal weakens (moving away from transmission antenna)
- How to correct
- Increase power of transmission
- Repeat signal from closer broadcast point (wireless range extender)
- Interference
- Wireless signals are vulnerable to noise
- SNR --> signal to noise ratio
- Refraction
- Alteration of direction, speed, and wavelength
- Happens when wave is traveling into/through different mediums
- Reflection
- Scattering
- Diffusion in multiple directions
- Diffraction
- Split into secondary waves
Topologies
- Different than wired networks because they are not bound by cabling paths
- Types
- Ad hoc
- Small number of nodes closely positioned
- No intervening connectivity device
- E.g. multiple computers directly communicating
- Infrastructure
- Uses intervening connectivity device
- Mesh
- Several APs work as peer devices on same network
- More fault-tolerant
Troubleshooting
- Tools
- Spectrum analyzer
- Assess the quality of wireless signals
- Wireless analyzer (Wi-Fi analyzer)
- Evaluate Wi-Fi network availability
- Optimize Wi-Fi signal settings
- Help identify Wi-Fi security threats
Networking Computer Science
