802.11
- WLANs work at physical layer and data link layer
- Support TCP/IP higher-layer OSI protocols and operating systems
- Most popular standard used by WLANs is wi-fi
- Developed by IEEE's 802.11 committee
- Standards
- 802.11b
- 802.11a
- 802.11g
- 802.11n
- 802.11ac
- Operates on 5 GHz
- Exceeds benchmarks set by earlier standards
- First Wi-Fi standard to approach Gigabit Ethernet capabilities
- 802.11n and later modify the way frames are used at the MAC sublayer
- LLC sublayer is primarily concerned with multiplexing, flow and error control, and reliability
Access Method
- 802.11 MAC services
- Append 48-bit physical addresses to frame to identify source/destination
- Same physical addressing scheme as other Ethernet networks
- Can be easily combined with IEEE networks
- Wireless devices
- Not designed to simultaneously send/receive
- Cannot prevent collisions
- Different access method than Ethernet
- CSMA/CA
- Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance
- Minimizes collision potential
- Uses ACK packets to verify every transmission
- More overhead than 802.3
- Real throughput is less than theoretical maximum
- RTS/CTS
- Request to Send/Clear to Send
- Ensures packets not inhibited by other transmissions
- Efficient for large transmission packets
- Decreases overall 802.11 efficiency
Frames
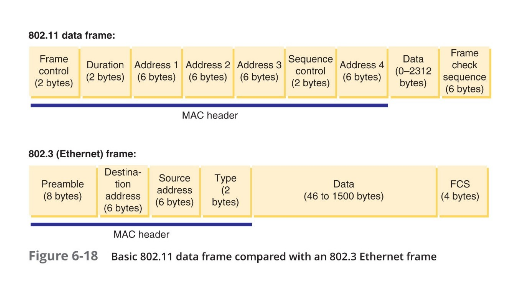
- Overhead
- Specifies MAC sublayer frame type
- Multiple frame type groups
- Management frames
- Association and re-association
- Control frames
- Medium access and data delivery
- ACK and RTS/CTS frames
- Data frames
- Carry data sent between stations
- Four address fields
- Source address
- Transmitter address
- Receiver address
- Destination address
- Sequence control field
- How large packets are fragmented
- Error checking and fragmentation are handled at the MAC sublayer of the data link layer
Innovations
- MIMO
- Multiple Input Multiple Output
- Multiple access point and client device antennas may issue signal to one or more receivers
- Increase range and network's throughput
- MU-MIMO
- Multiuser MIMO
- Newer tech that allows multiple antennas to service multiple clients simultaneously
- Reduces congestion
- Contributes to faster data transmission
- Available with WAVE 2 802.11ac products
- Channel bonding
- Two adjacent 20 MHz channels can be bonded to make a 40 MHz channel
- More than doubles bandwidth available in a single 20 MHz channel
- Frame aggregation
- Combine multiple frames into one larger frame
- Two techniques
- A-MSDU (Aggregated Mac Service Data Unit)
- A-MPDU (Aggregated Mac Protocol Data Unit)
- Reduces overhead
Computer Science Networking Wireless Networking
