Subnet Mask
- Used so devices can determine which part of an IP address is network ID and which part is host ID
- Number of 1s in subnet mask --> number of bits belonging to the network ID
- Number of 0s in subnet mask --> number of bits belonging to the host ID
- Example:
- IP address:
192.168.123.132
- Binary:
11000000.10101000.01111011.1000010
- Subnet mask:
255.255.255.0
- Binary:
11111111.111111111.111111111.00000000
- Network ID:
192.168.123.0
- Host ID:
0.0.0.132
- Useful for sending transmissions to another host
- Compares bits in its own network ID to bits in the network ID of destination host
- If bits match:
- Destination host on same network
- Sends transmission directly to destination host
- If bits don't match:
- Destination host on different network
- Sends transmission directly to default gateway on the network
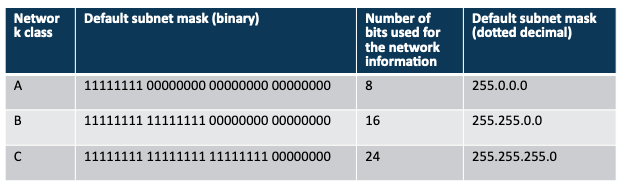
Subnet Mask Tables
- Class A, Class B, and Class C networks can be subnetted (subnetting)
- Each class --> different number of host info bits usable for subnet info
- Varies depending on network class and the way subnetting is used
Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM)
- Allows subnets to be further subdivided
- Smaller groupings until each subnet is about the same as the necessary IP address space
- Referred to as subnetting a subnet
Networking Computer Science
