Plate Tectonics
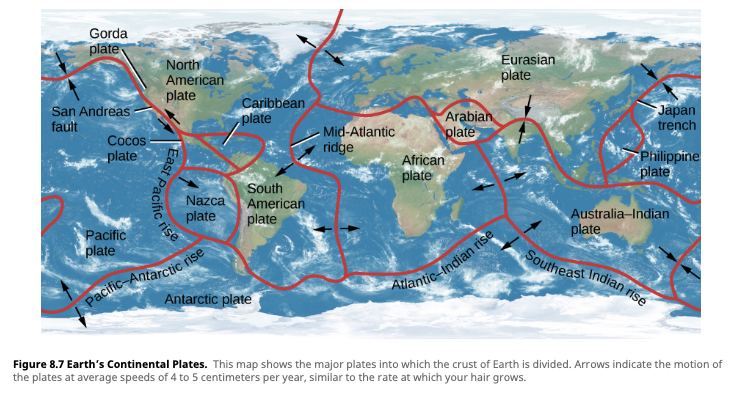
- Distinct boundaries of the Earth's crust
- Explains how slow motions within Earth's mantle move large segments of the crust
- Results in a gradual drifting of the continents
- Forms mountains and other large-scale geological features
- Cooling system for the planet
- Heat from inside --> outside
- There are ~12 tectonic plates on Earth
- Plates are moved by convection of the mantle
- Four basic interactions between plates at their boundaries
- Pull apart (rift zone)
- One plate burrows under another (subduction zone)
- Slide alongside each other (fault zone)
- Jam together
- Constantly renews Earth's crust and erases cratering events
Rift and Subduction Zones
- Rift zones
- Plates pull apart from each other
- Most found in the oceans
- Subduction zones
- Two plates come together, one is forced beneath another
- Thinner oceanic plates can be readily thrust down into upper mantle
- Often marked by ocean trenches
Fault Zones
- Crustal plates sliding parallel to each other
- Marked by cracks or faults
- Motion builds up stresses in the crust and released in sudden, violent slippages
- This generates earthquakes
- The longer the interval between earthquakes, the greater the stress and more energy released when the surface finally moves
Geology Earth
