Network Models
- Topology
- How parts of a whole work together
- Physical topology
- Mostly related to hardware
- How devices connect to form the physical network
- Logical topology
- How software connects to the network
- How users/programs gain access to the network
- Network operating system (NOS)
- Controls access to the entire network
- Required by client-server models
Peer-to-Peer Network Model
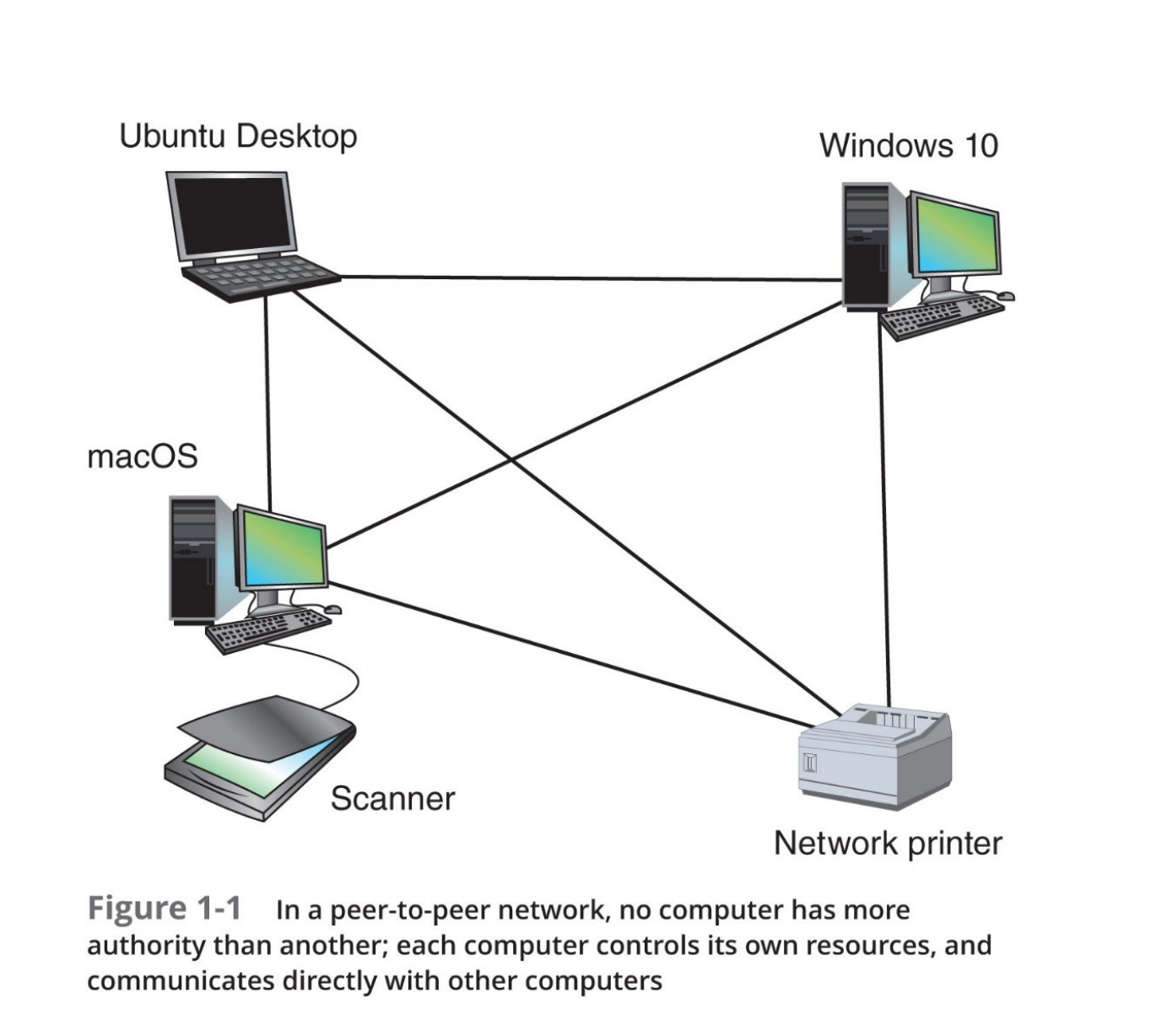
- OS of each computer on the network is responsible for controlling access to its resources
- Computers form logical groups and users
- Nodes or hosts
- May share resources (and control access to them)
Advantages
- Simple configuration
- Less expensive
Disadvantages
- Not scalable
- Not secure by default
- Not practical on a large scale
Client-Server Network Model
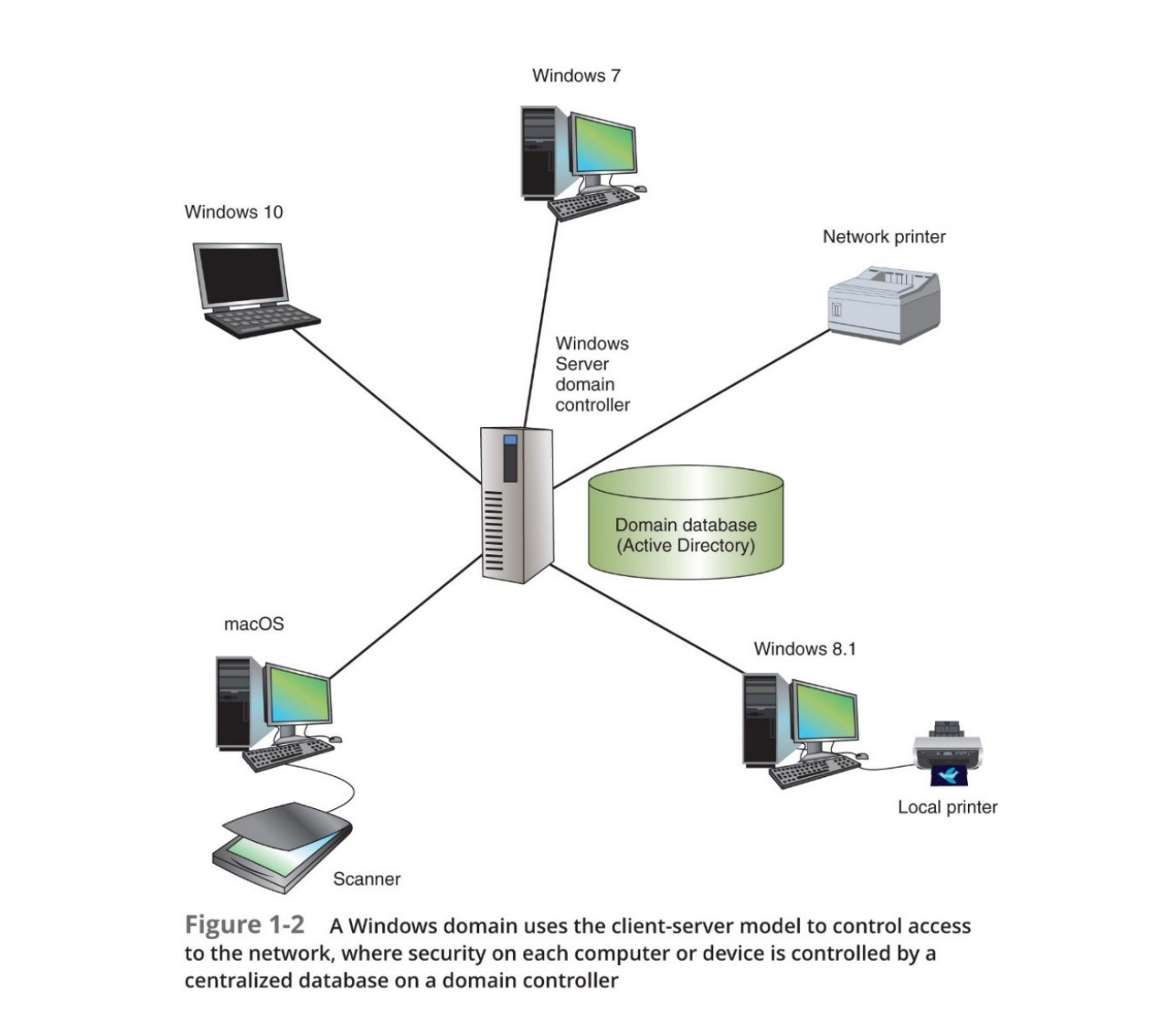
- Resources managed by NOS via centralized database
- In Windows it's Active Directory
- Client
- A computer making a request to another
- Resources aren't shared directly between clients
- Shared resources are on a server
- Access controlled by domain database
- NOS is responsible for:
- Managing client data and resources
- User, file, and network access
Advantages compared to peer-to-peer networks
- Credentials assigned in one place
- Shared resources are centrally controlled
- Central place for debugging, diagnostics, and correction
- More scalable
Computer Science Networking

